
Exploring the fundamentals of wireless charging for EV: Key Components and charging Steps of wireless charging systems for EV
Imagine never having to worry about charging your electric vehicle (EV) again. Just park, walk away, and let your car charge itself. This is the promise of wireless EV charging—a technology already making waves in Europe and Asia, and one that’s about to transform how Americans power their cars.
No more tangled cables, no more plugging in, just effortless charging every time you park. The future of EV charging is here, and it’s wireless.
According to market research projections, the global wireless EV charging market is expected to surpass the $825 million mark by 2027. Once considered futuristic technology, this innovation has now entered the stage of commercial application. So what exactly are the core components that make up this groundbreaking technology? And what engineering principles power its operation? Let's unveil the technical intricacies behind wireless charging systems.
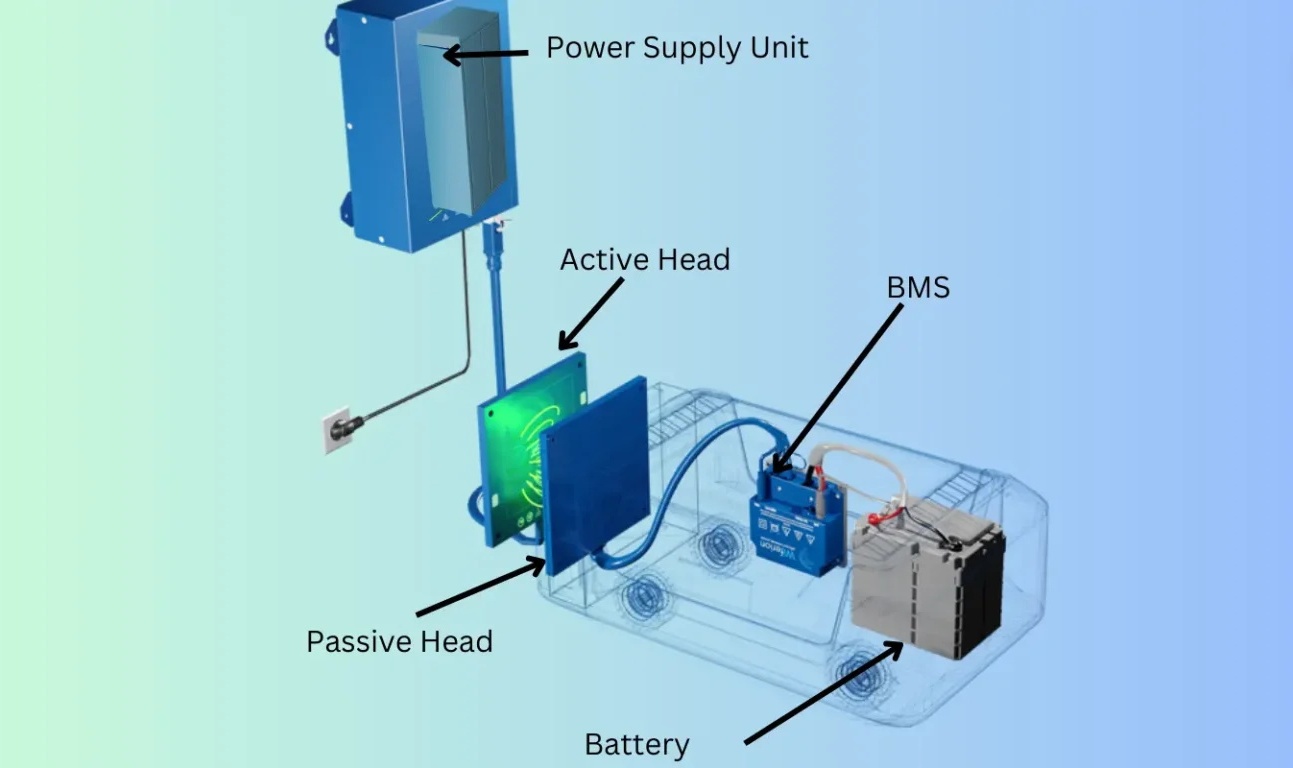
The wireless EV charging system uses resonant inductive coupling, with transmitter and receiver coils tuned to the same frequency for optimal power transfer. The system consists of:
Wall Box (Power Supply Unit)
● Contains high-power electronics to convert grid power to high-frequency energy.
● Includes MOSFETs, inverters, and control circuits.
● Supplies high-frequency energy to the charging pad.
Ground Assembly (Charging Pad / Active Pad)
● Installed on or in the ground.
● Generates a magnetic field for wireless power transfer.
● Features a primary coil, ferrite core, shielding, and resonant tuning.
● Converts high-frequency energy into a magnetic field.
Vehicle Assembly (Receiver Coil / Passive Pad)
● Mounted on the EV’s underside.
● Captures magnetic energy from the charging pad.
● Contains a secondary coil for energy reception.
● Requires proper alignment for efficient charging.
● Converts received energy to DC for battery charging.
Communication System
● Enables data exchange between vehicle and charger.
● Manages charging initiation, termination, and monitoring.
● Ensures safe and efficient power transfer.
Inductive charging is carried out through the wireless charging components mentioned above. Energy is transferred between two coils by using an electromagnetic field - one located on the ground charging pad and the other inside the vehicle.
Step 1: Charging Infrastructure Installation
● Charging Pad Setup: A ground-based pad (installed on or embedded in pavement) houses a primary coil that generates a magnetic field when powered.
● Power Conversion: The pad connects to an electronics cabinet that converts grid AC power into high-frequency AC for efficient wireless charging.
Step 2: Vehicle Preparation
● Receiver Coil: The EV has a secondary coil mounted underneath to capture the magnetic field from the charging pad.
● Power Conversion Module: An onboard unit converts the received AC power into DC to charge the battery.
Step 3: Vehicle Alignment
● Parking Over the Pad: The driver positions the EV over the charging pad. Some systems allow minor misalignment without significant efficiency loss.
● Automatic Detection: Advanced systems recognize the vehicle and initiate charging without driver input.
Step 4: Energy Transfer Begins
● Magnetic Field Activation: The charging pad’s primary coil generates a high-frequency magnetic field.
● Inductive Coupling: The receiver coil captures this energy via resonant inductive coupling (both coils tuned to the same frequency for maximum efficiency).
Step 5: Battery Charging Process
● AC to DC Conversion: The vehicle’s electronics convert the received AC power into DC to charge the battery.
● Real-Time Monitoring: The system adjusts power flow based on battery status, ensuring safe and efficient charging.
Step 6: Charging Completion
● Automatic Shutoff: Charging stops once the battery is full to prevent overcharging.
● Driver Notification: The system alerts the driver (via app or dashboard) when charging is complete.
Park and charge - no cables needed. This convenience is becoming a reality. With advancing technology, wireless charging is making EV ownership easier than ever. Already being tested in select regions, this innovation is expected to become mainstream within a few years. When you're ready for your next EV, will you choose one with wireless charging capability?
Contact Person: Miss. Kiki
| WhatsApp : | +8617763224709 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763224709 |
| WeChat : | +8617763224709 |
| Email : | kiki@lifepo4-battery.com |