The charger for new energy electric vehicles (EVs) is a crucial electric power conversion device designed specifically to charge the vehicle’s power battery. According to their installation location and functionality, chargers are mainly divided into on-board chargers and off-board chargers. This article explains the key differences between the two types from multiple perspectives.
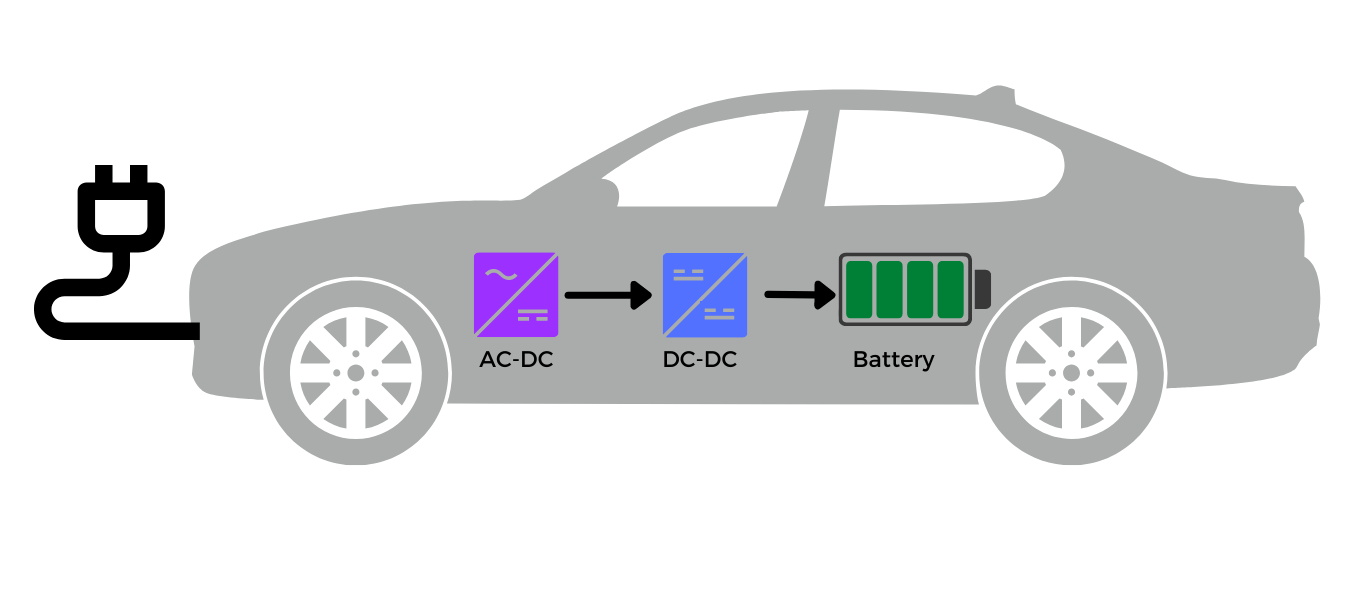
On-Board Charger:
Installed inside the electric vehicle itself. Due to space and weight limitations of the vehicle, on-board chargers are generally compact, lightweight, and have relatively low power.
Off-Board Charger:
Installed externally, outside the vehicle, typically in charging stations. Without vehicle size constraints, off-board chargers tend to be larger in volume and higher in power capacity.
● On-Board Charger:
Connects to an AC power source (single-phase 220V or three-phase 380V) via a plug and cable. It converts AC power into DC power suitable for charging the vehicle’s battery.
■ Also called AC charger or slow charger.
■ Advantages: Convenient charging wherever an AC power socket is available, helping extend battery life due to slow, controlled charging.
■ Disadvantages: Limited by vehicle space, generally low power output, resulting in slow charging and longer charge times.
● Off-Board Charger:
Connects directly to the AC power grid and converts AC to controllable DC power to charge the battery, commonly installed in DC charging piles.
■ Known as DC charger or fast charger.
■ Advantages: High power, can deliver large current for fast charging, significantly reducing charging time.
■ Disadvantages: Large size and weight, high construction costs, immobility, fewer available charging stations, and frequent fast charging may reduce battery lifespan.
■ Recommendation: Use slow charging as the primary method and fast charging as a supplement.
● On-Board Charger:
Comprises two main parts:
■ Power Circuit: Includes AC voltage regulator, transformer, and power transistors to convert AC to DC power.
■ Control Circuit: Communicates with the Battery Management System (BMS) to dynamically adjust voltage and current and control the charging process.
● Off-Board Charger:
Includes several modules such as power unit, control unit, metering unit, charging interface, power supply interface, and human-machine interface, designed for robust power conversion and user interaction.
On-board chargers offer high efficiency, reliability, safety, and ease of installation due to their compact design, with output power ranging from 2 kW to 40 kW. They meet the charging requirements for a wide range of vehicles including passenger cars, commercial vehicles, engineering machinery, special vehicles, and even shipborne applications.
TC Charger, based in China, has over 23 years of expertise in EV on-board charger development and manufacturing. Their factory spans over 2100 square meters with a standardized large-scale production line. Holding 2 technology invention patents and 16 utility model patents, TC Charger produces up to 60,000 units monthly. Their chargers are internationally certified, offering eco-friendly, high-efficiency solutions trusted by customers worldwide.
Feature | On-Board Charger | Off-Board Charger |
Installation | Inside the vehicle | Outside the vehicle (charging station) |
Power source | AC power converted onboard to DC | AC to DC conversion externally |
Power output | Low to medium (2kW-40kW) | High power for fast charging |
Charging speed | Slow charging | Fast charging |
Size & Weight | Compact and lightweight | Large and heavy |
Cost | Lower system cost | Higher construction and maintenance cost |
Mobility | Mobile with vehicle | Fixed installation |
Battery impact | Prolongs battery life | May reduce battery life if used frequently |
Next:none
Previous:REPT BATTERO Unveils Powtrix™ 6.26MWh Energy Storage System and 392Ah Cell at Intersolar Europe
Contact Person: Miss. Kiki
| WhatsApp : | +8617763224709 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763224709 |
| WeChat : | +8617763224709 |
| Email : | kiki@lifepo4-battery.com |