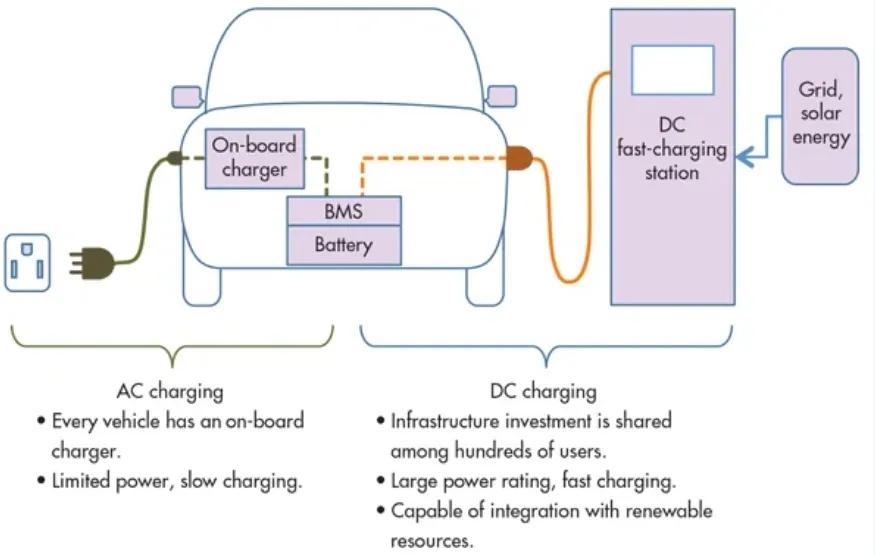
Electric vehicles (EVs) depend on a sophisticated network of components to operate efficiently, and two of the most essential are the on-board charger (OBC) and the DC converter. Although both are vital to an EV’s power system, they perform very different roles. Getting to know these differences can help you make smarter decisions about your vehicle’s charging and power management.
The on-board charger is designed to convert alternating current (AC) from an external power source—such as a charging station—into direct current (DC) to recharge the vehicle’s battery. It essentially acts as the bridge between the power grid and the EV, making sure the battery gets the right voltage and current for safe and efficient charging.
Key features of an on-board charger include:
- AC to DC conversion
- Charging speed control
- Safety mechanisms (e.g., overvoltage protection and thermal management)
On the other hand, the DC converter is responsible for managing and distributing power inside the vehicle. It takes the high-voltage DC power from the battery and steps it down to lower-voltage DC power, which is used to run various electronic systems like the lights, infotainment, and sensors.
Key features of a DC converter include:
- Voltage regulation
- Power distribution
- Energy efficiency optimization
In an electric vehicle, the on-board charger and DC converter work hand-in-hand to keep everything running smoothly. The OBC focuses on charging the battery, while the DC converter makes sure all the auxiliary systems get the power they need. Together, these two components form the backbone of the EV’s electrical system.
Contact Person: Miss. Kiki
| WhatsApp : | +8617763224709 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763224709 |
| WeChat : | +8617763224709 |
| Email : | kiki@lifepo4-battery.com |