
If you own or are considering an electric vehicle (EV), you’re probably familiar with terms like “range,” “battery size,” and “fast charging.” But there’s a silent hero working behind the scenes every time you plug in at home: the on-board charger (OBC).
Understanding your EV’s on-board charger is key to grasping your vehicle’s full capabilities—and its limitations. Let’s explore what it is, how it works, and why it matters.
In simple terms, the on-board charger is a critical component built into your electric vehicle. Its main job is to convert alternating current (AC) electricity—from your home charging unit or public station—into direct current (DC) electricity, which is what your car’s battery stores and uses.
Think of it as a sophisticated translator. The grid “speaks” AC, but your EV’s battery only “understands” DC. The onboard charger serves as that essential interpreter, enabling safe and efficient energy transfer.
The process is a marvel of modern engineering. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
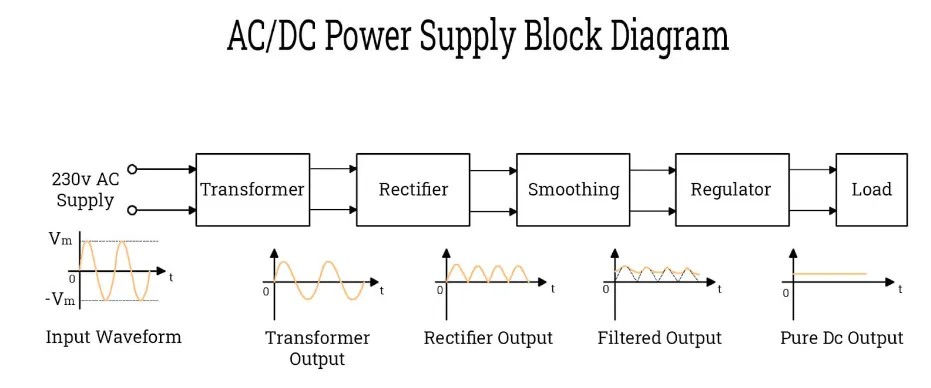
1. AC Input: You connect your EV to an AC power source, such as a Level 1 or Level 2 charger.
2. Conversion: The on-board charger receives AC power and rectifies it, turning it into DC power.
3. Regulation: It carefully adjusts the voltage and current of the DC power to meet the specific requirements of your lithium-ion battery pack.
4. Communication: Throughout the process, the OBC constantly communicates with both the charging station and the vehicle’s Battery Management System (BMS) to ensure safety, efficiency, and optimal temperature control.
When evaluating an EV, pay attention to these core specs of the on-board charger:
- Power Rating (kW): This determines your AC charging speed. A higher kW rating means faster charging. Common ratings include 3.3 kW, 7.4 kW, 11 kW, and 22 kW.
- Efficiency: This refers to how much energy is lost as heat during the AC-to-DC conversion. Higher efficiency (e.g., 92–94%) means more energy makes it to your battery—saving you money over time.
- Number of Phases: This indicates the type of power input the charger can handle. Most home chargers use single-phase power, while higher-power units may require a three-phase supply.
Without an OBC, you can’t charge your EV using standard AC power. While DC fast chargers bypass the onboard charger by supplying DC power directly to the battery, they are costly and less suitable for everyday use. The OBC is what makes convenient overnight charging at home or work possible.
A high-power onboard charger is also a major quality-of-life feature—it significantly reduces the amount of time needed to fully recharge your battery.
On-board charger technology is continuously advancing, becoming more powerful, efficient, and compact. Whether you’re an OEM, developer, or EV enthusiast, understanding this core component is essential.
At www.evlithiumcharger.com, we specialize in providing cutting-edge on-board charger solutions and insights. From the latest innovations and technical deep dives to industry updates—we’re your trusted source for all things OBC.
Contact Person: Miss. Kiki
| WhatsApp : | +8617763224709 |
|---|---|
| Skype : | +8617763224709 |
| WeChat : | +8617763224709 |
| Email : | kiki@lifepo4-battery.com |